Psoriasis is a long-lasting, chronic skin disease.
The reason for the development of the disease
Psoriasis occurs due to a pathology of skin cells, when the top layer of the skin dies within 4-5 days, when it is usually a few weeks. The cause of the disease is not fully understood, but doctors have identified several factors that cause the disease:
- Hereditary predisposition - the disease manifests itself in a young age, starting at 15 years old and is more often hereditary. If one of the parents has been diagnosed with psoriasis, the child is more than 50% more likely to have it.
- Autoimmune Conflict - with this type of disorder, the body's immune cells stop recognizing skin cells as part of the body, starting to attack them as foreign elements.
- Neurological shocks - contribute to the release of hormones into the bloodstream, leading to metabolic disorders and provoking the development of the disease.
- Disrupts the hormonal balance and metabolism.
Psoriasis is not contagious, since there are no infectious agents that can transmit it.
Psoriasis Symptoms
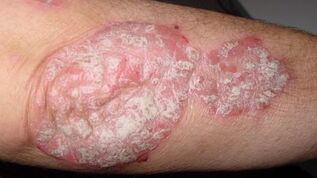
The main symptoms of the disease are a characteristic skin rash, which primarily affects the inner surface of the elbow and knee joints, as well as areas of the skin that are frequently injured by friction.
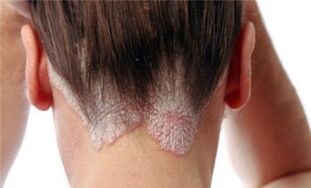
A rash along the edge of the scalp and other less typical spots may also occur.
A skin rash that appears as patches covered with gray or white scales. Skin rashes in psoriasis have three characteristic characteristics:
- Stearin Spot Symptoms:Easily peels off a white scaly, which looks like a wax crumble.
- Head membrane- after the scales have been removed, a white film can be seen under them covering the spot surface.
- Bleeding spot- when scratching the spot, the end membrane comes off, the papillae are damaged, on which small drops of blood stick out.
In the first stage, around the papillae forms a pale rim, this stage does not have phenomenon of peeling. The pallor around the stain is the body's response to the rejection of the epidermis. The disease is accompanied by severe itchy skin, cracks and mild bleeding on the skin when scratching. Secondary infection can join, penetrate through the damaged skin.
In addition to the skin, psoriasis also affects the nails, causing the nail plates to become fragile, with horizontal lines and concave areas.
Autoimmune conflicts can affect joints, causing joint-like pain, especially in the knuckles.
Types of psoriasis
Psoriasis first occurs in people under the age of 30, it is an inherited disease that primarily affects the skin and has a typical atopic.
Psoriasis of the second type affects people over the age of forties and is not inherited. It often affects nail and scalp plates, small and tear-shaped rashes. Disease in elderly patients is caused by impaired immunity against chronic infectious diseases and improper lifestyle.
Clinical studies have confirmed an association between psoriasis type 2 with alcohol and unhealthy food abuse.
Types of psoriasis
Psoriasis comes in several forms with different severity:
- Plaque psoriasis- characteristic papules that form on the skin, accompanied by itching and peeling.
- Pustular formwhich is characterized by the appearance of bubbles, surrounding redness, intense itching and burning, is considered to be a moderate form of the disease.
- Erythrodermais characterized by large lesions of the skin, accompanied by oozing and multi-epidermal secretions, which are particularly difficult to tolerate, often accompanied by pustular lesions and fungal infections.
Stages of psoriasis
The disease develops in many stages:
- Early stagesignals the onset of the disease, in this stage, rarely appears some pale spots, the skin begins to peel off.
- Active phaseis accompanied by severe symptoms, severe scaling, itching and inflammation.
- Static phase- indicates remission, flaking at this stage practically stops, instead a spot, pigmentation or pseudo-pale areas are formed.
Diagnosis of psoriasis
To make a diagnosis, you must consult a dermatologist. Pathology has a clear clinical picture, which is confirmed by a medical history and biopsy of skin factors with their follow-up study.
Treatment of psoriasis
Treatment of the disease needs to be taken in a holistic manner, at the same time preventing external symptoms and impacting on the underlying cause of the disease.
Drug treatment
In extreme cases, measures are taken to reduce the body's immune attack on its own cells:
- cytostatics;
- Antihistamines;
- Corticosteroid hormone;
- Intestinal sorbents and hepatoprotectants used to restore metabolism.
At the same time, measures are being taken to saturate the body with essential vitamins and trace elements:
- Silicon is one of the important trace minerals responsible for hormone balance and skin health.
- Calcium and vitamin D3 are needed to bring the disease into remission. Prescribe together to increase calcium absorption.
Spot Remedy
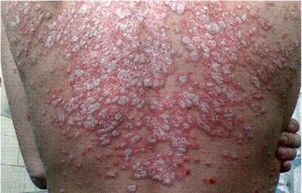
For skin protection, external agents are used in the form of ointments and creams:
- Glucocorticoid, which reduces the immune response, also reduces inflammatory symptoms, itching and swelling of the skin.
- Salicylic acid and herbal products are needed to moisturize the skin and protect against secondary infections.
- Topical cytostatics should be used only during the active disease phase.
Procedure
To speed up the healing process, physiological tricks are prescribed:
- Cryotherapy;
- UV radiation;
- Laser treatment.
If necessary, plasmapheresis is performed to clean the plasma and stabilize the cell.
Precautions
If the trend of the disease can be identified, there are some precautions that should be taken:
- Practice a healthy lifestyle, stop smoking and alcohol;
- Build a daily routine, avoid stress, approach rational organization of work schedule;
- Follow the diet, giving up too much carbohydrates, spices and fatty foods. It is advisable to avoid preservatives and ready-to-eat foods;
- Spend enough time outdoors;
- Use specially selected pH-value soaps and shampoos, do not use hard towels and towels, and dry skin after bathing;
- Wear natural materials that are not too close to your body;
- Have regular checkups, control hormone levels in the blood and, if necessary, initiate treatment early.
Such measures will help maintain healthy skin and significantly improve quality of life.

























